About the Department
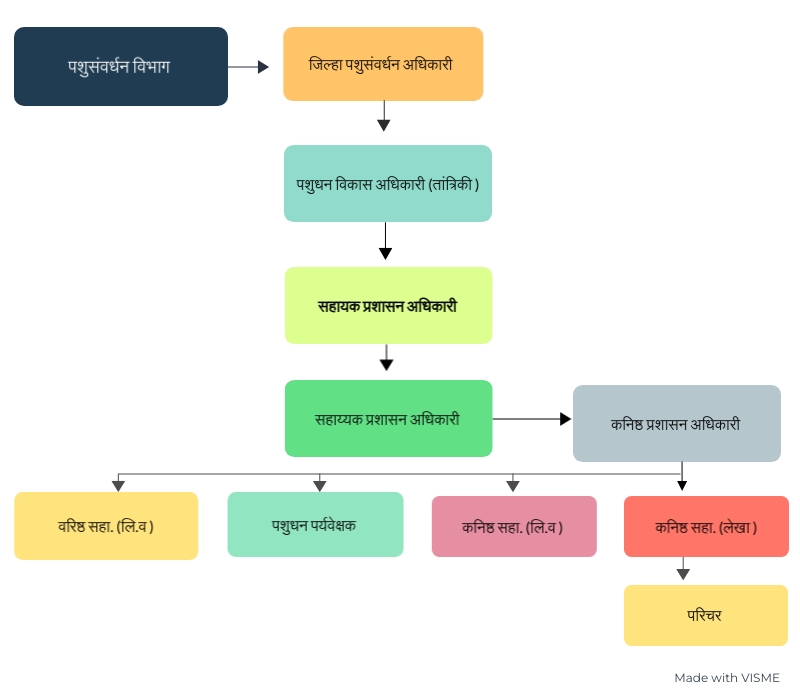
The Head of Animal Husbandry Department is a Class 1 Officer of the State Government. He has the designation of District Animal Husbandry Officer. Many State and Central Government schemes are effectively implemented through this department to increase animal husbandry and milk production. There are Veterinary Clinics Category 1 – 27 and Category 2 – 37 in the district. In this, a doctor is appointed through the state government and is designated as Livestock Development Officer. Also Livestock Development Authority (Extension) is working as head in Panchayat Samiti level office.
Vairan Development Program:-
Objective:- 70% of the expenses of a livestock farmer are spent on animal feed and fodder and good scientific nutrition is the key to the livestock farmer. Therefore, to limit the expenses, the best solution is to buy high quality animal feed.
Types of fodder:-
1. Monocot fodder includes sorghum, maize, multicut millet etc. These fodder crops provide large amounts of carbohydrates and fiber to the animals, which increases milk production and milk fat.
2. Multicot fodder: – These include barley, chickpea, lucerne etc. These fodder crops provide high quality protein to the animals and increase the amount of SNF in the milk.
3. Perennial Grass: – These include Hybrid Napier (Variants-CO4, DHN-6, HN-10, Super Napier etc. and Nutrifeed etc. fodder crops. The fodder production per acre of these fodder crops is record and it provides green fodder to the animals throughout the year.
1. District Annual Plan-General: – In order to provide good quality green fodder to the animals under the scheme, M.P. Chari, Maize, Maldandi, Barseem seeds or Hybrid Napier, Nutrifeed or Thombe are distributed on 100 percent subsidy during Kharif and Rabi seasons subject to the provisions available under the District Annual Plan. The beneficiaries of this scheme can avail the benefit of all castes/tribes.
2. Vidarbha Marathwada Milk Development Project (NDDB): –
- Kadaba Kutti Machine: After the fodder crops reach flowering stage, all the necessary nutrients are stored in them. Therefore, by grinding such large grasses into small pieces and feeding them with Kadaba Kutti machine, the amount of fodder is fully utilized and the amount of wastage is reduced. Under the Vidarbha Marathwada Dairy Development Project, a government subsidy of 50% or a maximum of Rs. 8000/- is given on the purchase of this machine.
- Production of green fodder: A simple solution to increase the nutritional value of green fodder and to make green fodder available throughout the year is to produce green fodder. By grinding carbohydrate-free fodder like maize, jowar, bajra, hybrid Napier grass etc. and keeping it in an airtight large plastic bag, the action of bacteria causes limited acid formation in the fodder and the fodder can be stored throughout the year. This improves the quality of the fodder (Nutritional value enhanced). Also, feeding green fodder is more beneficial than green fodder. Government subsidy of 60% or Rs. 3600/- is given on the purchase of green fodder bags under the Vidarbha Marathwada Dairy Development Project.
Benefits of fodder crops:-
- Being a perennial grass, regular green fodder is available throughout the year. Once planted, green fodder is supplied for 5 to 6 years. Unlike seasonal fodder crops, there is no cost of cultivation, thus saving on production costs.
- Hybrid Napier is a variety developed from a cross between millet and Napier and is nutritious and high yielding. The average height of Napier grass is up to 10 feet and the number of shoots per stem is 30-40. The production of green fodder is 180-200 MT per year.
- The protein content is 10-12% and the oxalic acid content is very low. Since there are no harmful ingredients, there is no harm to the animals.
- The stalk is soft and juicy compared to other hybrid Napier varieties, so there is no problem while harvesting the fodder. The fodder can be fed to the animals without chopping it without a chaff cutter. This saves on cost and manpower and no part of the fodder is wasted.
- The animals are eating the fodder with gusto, and high-quality fodder can be produced from it.